Update 2017-1-24: Code Sample is on github, view it here
What will you do when you want to remove simple background on an image?
First thing you may come up is “Simple, replace background color with transparent”.
@interface UIImage (BackgroundRemoval)
//Simple Removal
- (UIImage *)simpleRemoveBackgroundColor;
@end
@implementation UIImage (BackgroundRemoval)
- (UIImage *)simpleRemoveBackgroundColor{
CGImageRef rawImageRef=self.CGImage;
const CGFloat colorMasking[6] = {250, 255, 250, 255, 250, 255};
UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(self.size);
CGImageRef maskedImageRef=CGImageCreateWithMaskingColors(rawImageRef, colorMasking);
{
//if in iphone
CGContextTranslateCTM(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(), 0.0, self.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(), 1.0, -1.0);
}
CGContextDrawImage(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(), CGRectMake(0, 0, self.size.width, self.size.height), maskedImageRef);
CGContextSetInterpolationQuality( UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext() , kCGInterpolationHigh );
CGContextSetAllowsAntialiasing(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(), true);
CGContextSetShouldAntialias(UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext(), true);
UIImage *result = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
CGImageRelease(maskedImageRef);
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
return result;
}
@end“Easy, right?”
What if the object you want to extract is mainly that color?
For Example:
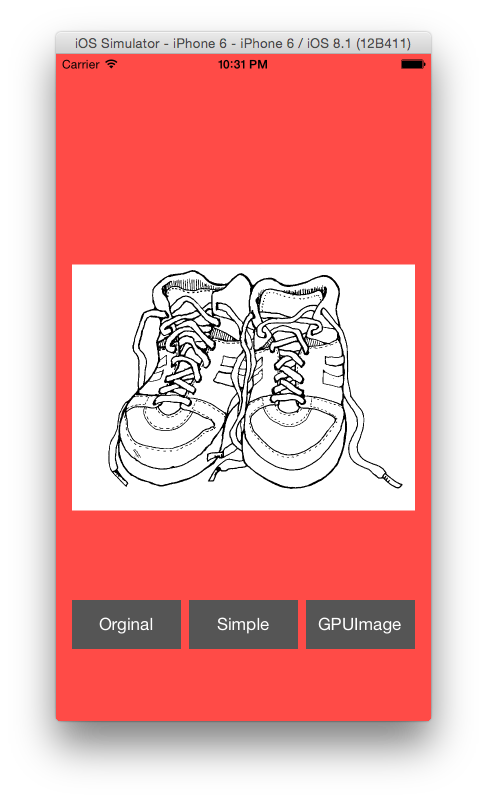
By Replacing the background color, you will get this:
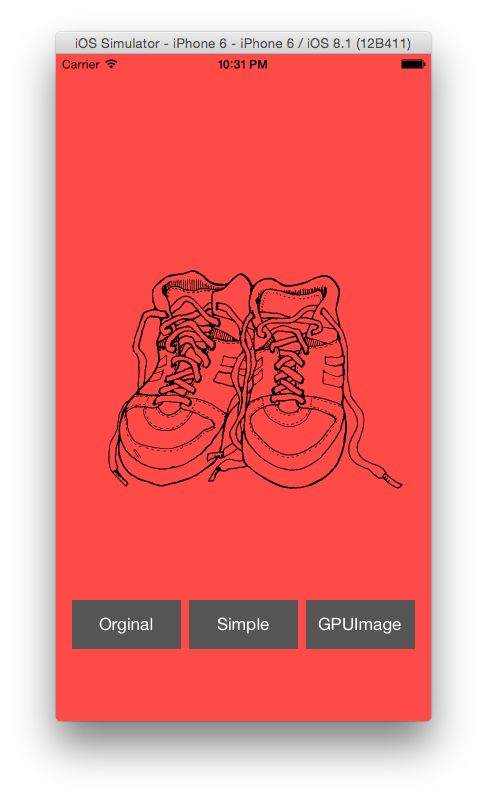
“So, What do we do?”
Flood fill + Alpha Mask
###Steps
-
Flood fill with magneta color 1
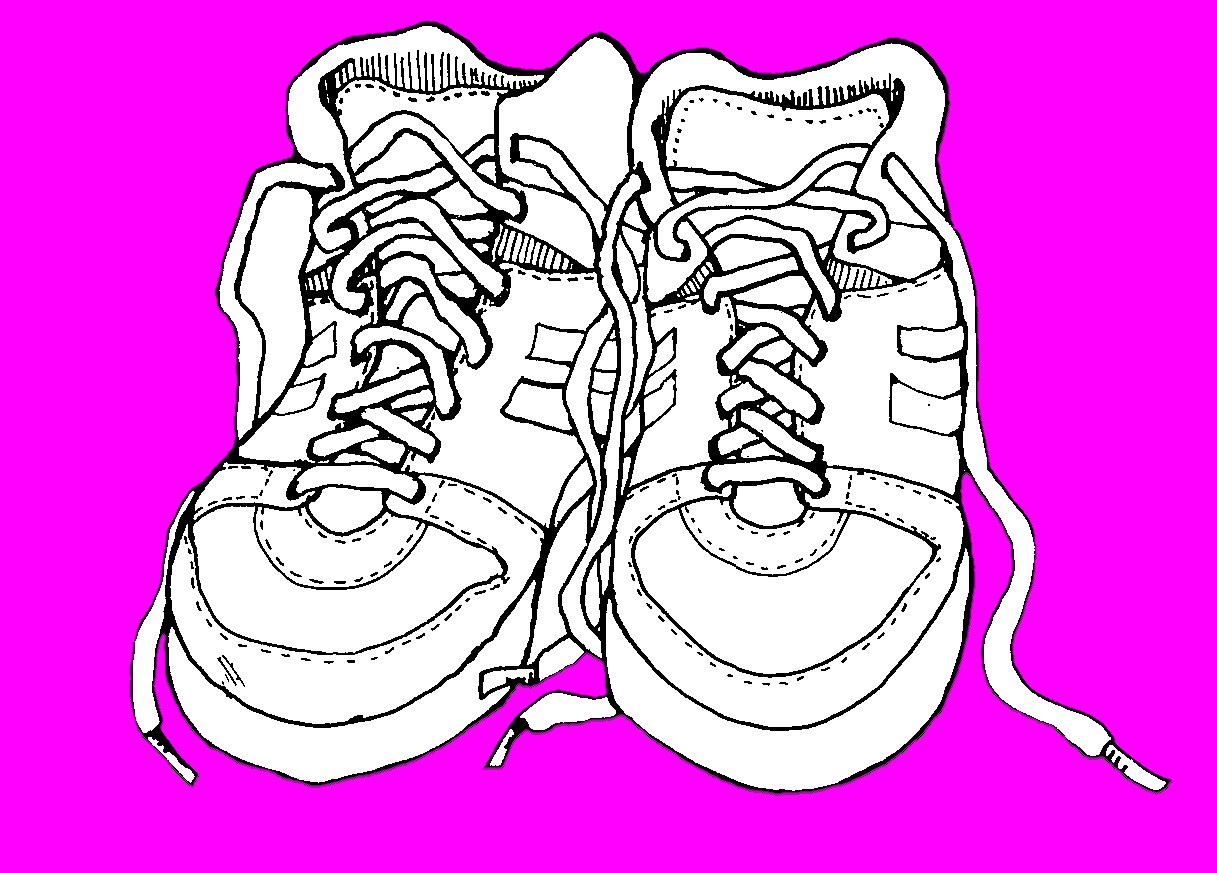

-
Scan through each pixels, if it is magneta color, change it with transparent, otherwise change it to black

-
Mask the orginal image with the masks
-
Finish!
#import "UIImage+FloodFill.h"
//https://github.com/Chintan-Dave/UIImageScanlineFloodfill
#define Mask8(x) ( (x) & 0xFF )
#define R(x) ( Mask8(x) )
#define G(x) ( Mask8(x >> 8 ) )
#define B(x) ( Mask8(x >> 16) )
#define A(x) ( Mask8(x >> 24) )
#define RGBAMake(r, g, b, a) ( Mask8(r) | Mask8(g) << 8 | Mask8(b) << 16 | Mask8(a) << 24 )
@interface UIImage (BackgroundRemoval)
//Simple Removal
- (UIImage *)floodFillRemoveBackgroundColor;
@end
@implementation UIImage (BackgroundRemoval)
- (UIImage*) maskImageWithMask:(UIImage *)maskImage {
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
CGImageRef maskImageRef = [maskImage CGImage];
// create a bitmap graphics context the size of the image
CGContextRef mainViewContentContext = CGBitmapContextCreate (NULL, maskImage.size.width, maskImage.size.height, 8, 0, colorSpace, (CGBitmapInfo)kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast);
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
if (mainViewContentContext==NULL)
return NULL;
CGFloat ratio = 0;
ratio = maskImage.size.width/ self.size.width;
if(ratio * self.size.height < maskImage.size.height) {
ratio = maskImage.size.height/ self.size.height;
}
CGRect rect1 = { {0, 0}, {maskImage.size.width, maskImage.size.height} };
CGRect rect2 = { {-((self.size.width*ratio)-maskImage.size.width)/2 , -((self.size.height*ratio)-maskImage.size.height)/2}, {self.size.width*ratio, self.size.height*ratio} };
CGContextClipToMask(mainViewContentContext, rect1, maskImageRef);
CGContextDrawImage(mainViewContentContext, rect2, self.CGImage);
// Create CGImageRef of the main view bitmap content, and then
// release that bitmap context
CGImageRef newImage = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(mainViewContentContext);
CGContextRelease(mainViewContentContext);
UIImage *theImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:newImage];
CGImageRelease(newImage);
// return the image
return theImage;
}
- (UIImage *)floodFillRemove{
//1
UIImage *processedImage = [self floodFillFromPoint:CGPointMake(0, 0) withColor:[UIColor magentaColor] andTolerance:0];
CGImageRef inputCGImage=processedImage.CGImage;
UInt32 * inputPixels;
NSUInteger inputWidth = CGImageGetWidth(inputCGImage);
NSUInteger inputHeight = CGImageGetHeight(inputCGImage);
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
NSUInteger bytesPerPixel = 4;
NSUInteger bitsPerComponent = 8;
NSUInteger inputBytesPerRow = bytesPerPixel * inputWidth;
inputPixels = (UInt32 *)calloc(inputHeight * inputWidth, sizeof(UInt32));
CGContextRef context = CGBitmapContextCreate(inputPixels, inputWidth, inputHeight, bitsPerComponent, inputBytesPerRow, colorSpace, kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast | kCGBitmapByteOrder32Big);
CGContextDrawImage(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, inputWidth, inputHeight), inputCGImage);
//2
for (NSUInteger j = 0; j < inputHeight; j++) {
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < inputWidth; i++) {
UInt32 * currentPixel = inputPixels + (j * inputWidth) + i;
UInt32 color = *currentPixel;
if (R(color) == 255 && G(color) == 0 && B(color) == 255) {
*currentPixel = RGBAMake(0, 0, 0, A(0));
}else{
*currentPixel = RGBAMake(R(color), G(color), B(color), A(color));
}
}
}
CGImageRef newCGImage = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(context);
//3
UIImage * maskImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:newCGImage];
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
CGContextRelease(context);
free(inputPixels);
UIImage *result = [self maskImageWithMask:maskImage];
//4
return result;
}
@endGradient Background
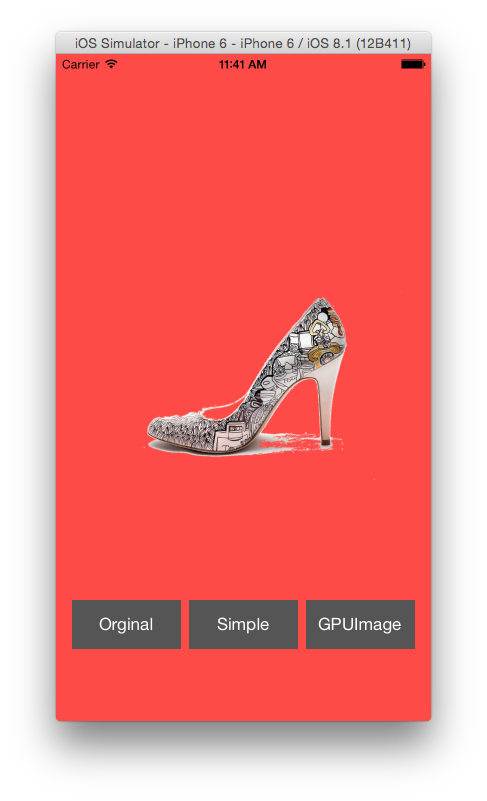
What about image with gradient background?
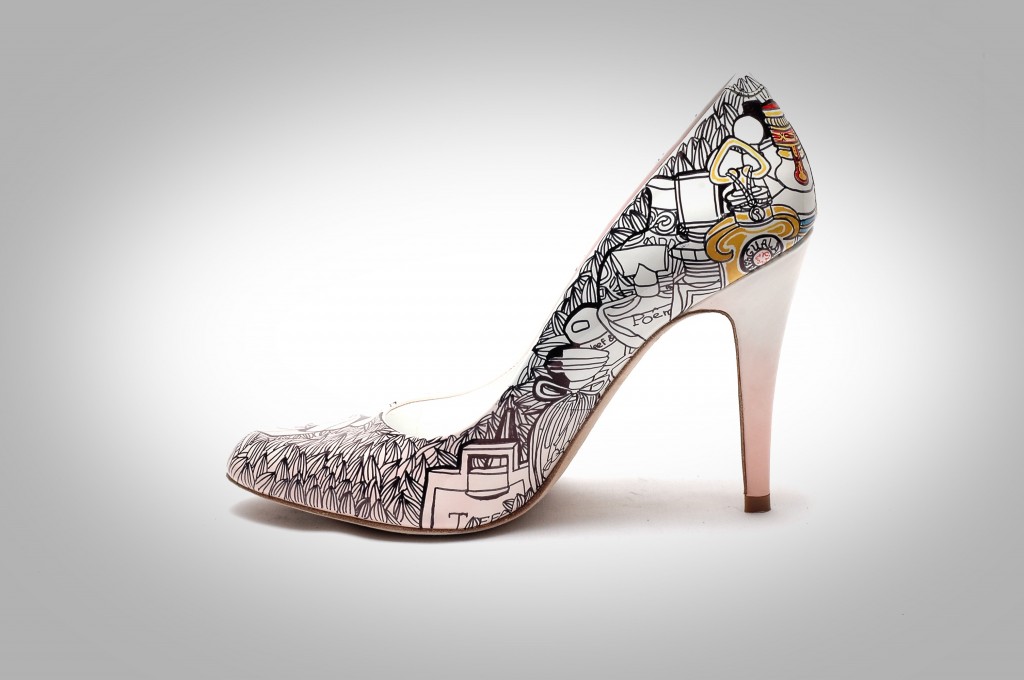

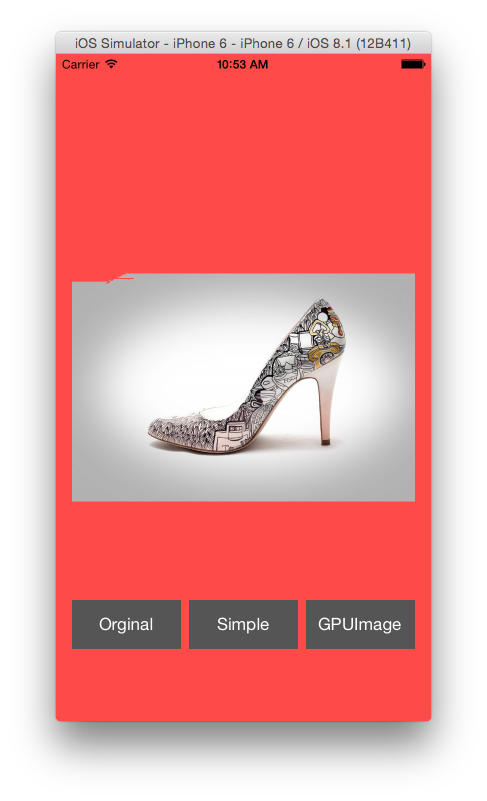 Hmm…Not so great.
Hmm…Not so great.
In this case, we can use some edge detection. Here comes GPUImage.
The GPUImage framework is a BSD-licensed iOS library that lets you apply GPU-accelerated filters and other effects to images, live camera video, and movies. In comparison to Core Image (part of iOS 5.0), GPUImage allows you to write your own custom filters, supports deployment to iOS 4.0, and has a simpler interface. However, it currently lacks some of the more advanced features of Core Image, such as facial detection.
###Steps
-
Detect Edge Using GPUImage
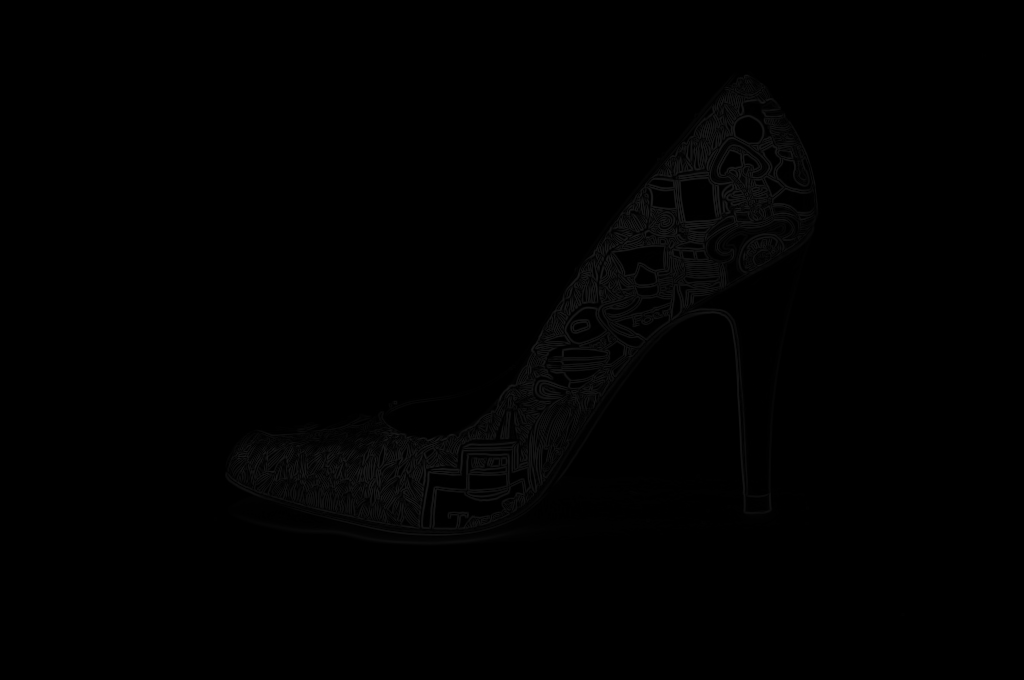

-
Flood fill
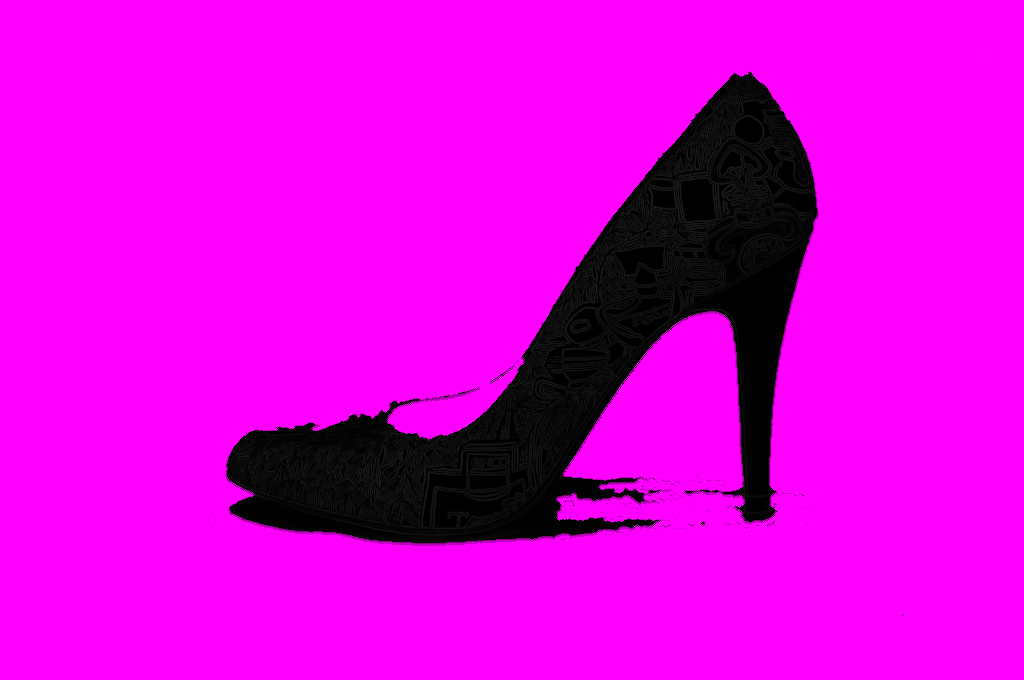

-
Create Mask
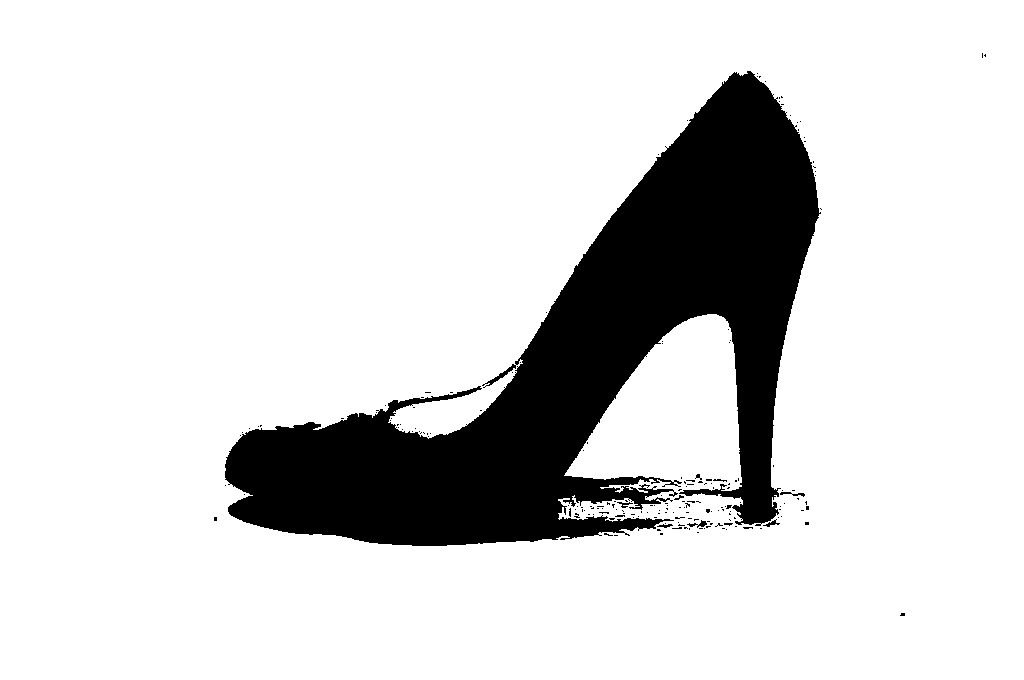

-
Mask It
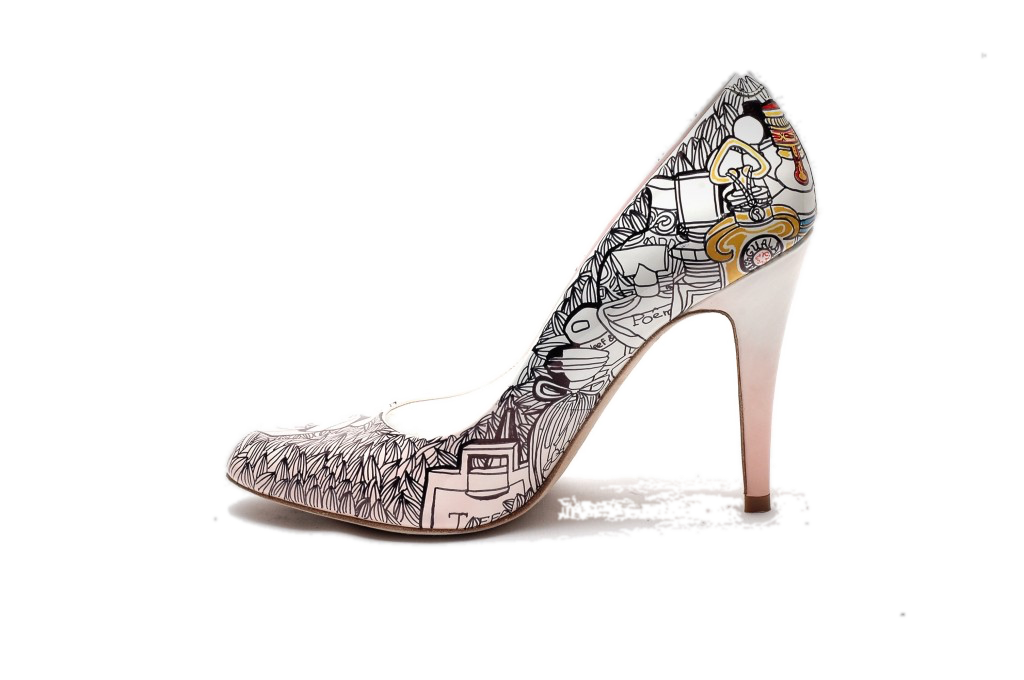

-
Finish!
- (UIImage *)complexReoveBackground{
GPUImagePicture *stillImageSource = [[GPUImagePicture alloc] initWithImage:self];
GPUImagePrewittEdgeDetectionFilter *filter = [[GPUImagePrewittEdgeDetectionFilter alloc] init];
[filter setEdgeStrength:0.04];
[stillImageSource addTarget:filter];
[filter useNextFrameForImageCapture];
[stillImageSource processImage];
UIImage *resultImage = [filter imageFromCurrentFramebuffer];
UIImage *processedImage = [resultImage floodFillFromPoint:CGPointMake(0, 0) withColor:[UIColor magentaColor] andTolerance:0];
CGImageRef inputCGImage=processedImage.CGImage;
UInt32 * inputPixels;
NSUInteger inputWidth = CGImageGetWidth(inputCGImage);
NSUInteger inputHeight = CGImageGetHeight(inputCGImage);
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
NSUInteger bytesPerPixel = 4;
NSUInteger bitsPerComponent = 8;
NSUInteger inputBytesPerRow = bytesPerPixel * inputWidth;
inputPixels = (UInt32 *)calloc(inputHeight * inputWidth, sizeof(UInt32));
CGContextRef context = CGBitmapContextCreate(inputPixels, inputWidth, inputHeight, bitsPerComponent, inputBytesPerRow, colorSpace, kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast | kCGBitmapByteOrder32Big);
CGContextDrawImage(context, CGRectMake(0, 0, inputWidth, inputHeight), inputCGImage);
for (NSUInteger j = 0; j < inputHeight; j++) {
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < inputWidth; i++) {
UInt32 * currentPixel = inputPixels + (j * inputWidth) + i;
UInt32 color = *currentPixel;
if (R(color) == 255 && G(color) == 0 && B(color) == 255) {
*currentPixel = RGBAMake(0, 0, 0, A(0));
}else{
*currentPixel = RGBAMake(0, 0, 0, 255);
}
}
}
CGImageRef newCGImage = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(context);
UIImage * maskImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:newCGImage];
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpace);
CGContextRelease(context);
free(inputPixels);
GPUImagePicture *maskImageSource = [[GPUImagePicture alloc] initWithImage:maskImage];
GPUImageGaussianBlurFilter *blurFilter = [[GPUImageGaussianBlurFilter alloc] init];
[blurFilter setBlurRadiusInPixels:0.7];
[maskImageSource addTarget:blurFilter];
[blurFilter useNextFrameForImageCapture];
[maskImageSource processImage];
UIImage *blurMaskImage = [blurFilter imageFromCurrentFramebuffer];
//return blurMaskImage;
UIImage *result = [self maskImageWithMask:blurMaskImage];
return result;
}Reference
Remarks
-
In fact, you can skip 2-3 if you find a way to flood fill
clearColorto UIImage, but I found out that flood fillingclearColorwill just fillblackColoron to image, so we need to use alpha mask on the image. ↩